
FBS turns 16
July 28, 2025
Basics
Mean Reversion and How to Use It in Forex Trading

“Mean” is the average price of an asset over a period of time. Mean reversion is a theory that stipulates that asset prices tend to reverseback to their long-term mean after extreme price moves because such trends can’t be sustained for too long. Mean reversion can apply to stocks, but also options, ETFs, commodities, volatility, earnings, and Forex trading.
Prices move in cycles, always oscillating around the average. If a price moves above the average, it will inevitably come back down below it, then back up, and so on. In this way, the mean functions kind of like a magnet, pulling prices back up or down if they go too far. Another way to see it is like a rubber band being stretched as prices move up or down, before the tension draws them back towards the mean.
A mean can be either dynamic or static. For a dynamic mean, the average is continuously updated because new data comes in. When you take a 20- or 50-day moving average, for example, the mean changes every day as the oldest day is dropped from the calculation and the most recent day is added. A static mean instead refers to an unchanging average that is calculated over a specific period, such as the average price over the last 5 days.
Mean reversion is a type of technical analysis (TA): it is part of a strategy that uses economic indicators and technical tools like historical data, moving averages, RSI, Bollinger Bands, and price patterns to study price behavior and identify opportunities.
Mean reversion strategy
Mean reversion strategy consists of making money on price swings by identifying overvalued or undervalued assets and assuming that prices will eventually return to historically average levels. Whereas trend-following consists of making money by following a trend, mean reversion consists of making money on deviations from a price mean.
Traders will implement this strategy to determine entry points for their positions. They can look at the moving average and use indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) to check how overbought or oversold the asset is, or Bollinger Bands to see how far the price has deviated from the mean. If the price is very high compared to the dynamic mean, or average, this can indicate a good time to sell. If the price falls below it, that might signal a good time to buy in. The further away the price gets from the mean, the more likely it is to reverse course.
How to use mean reversion in Forex trading
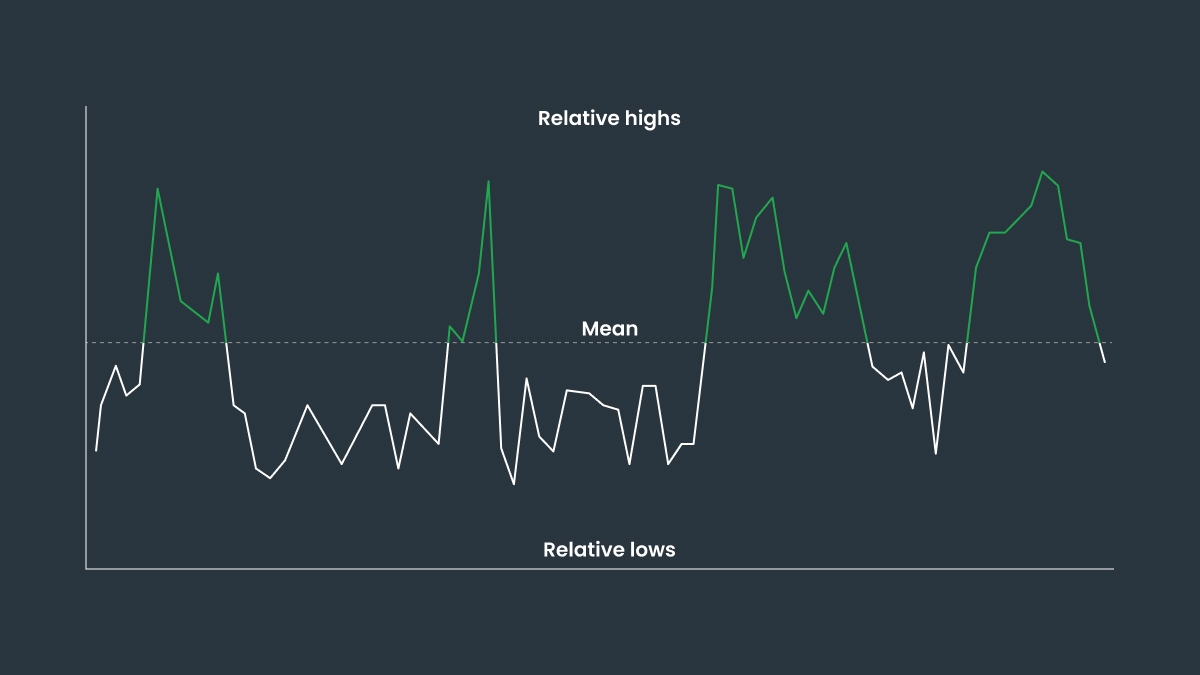
Mean reversion is very common in Forex trading. It’s a good way to identify opportunities for short-term positions. The strategy is to identify how far the currency pair usually deviates from its historical or average exchange rate, to get an idea of the range.
When the rate has deviated far enough, you can use technical analysis indicators to check for confirmation. The RSI and Stochastic Oscillator are momentum indicators that will show how overbought or oversold a currency pair is.
Pivot points are another technical analysis tool that traders use to check for any resistance or support levels that can signal that the price is ready to reverse. These are calculated using the highs, lows, and closing prices from the previous trading day.
Another tool that can be used in mean reversion for Forex trading is currency correlation. Some currency pairs are correlated in the sense that they usually move in the same direction. The EURUSD and GBPUSD pairs, for example, tend to move in the same direction because the Eurozone and the UK have close economic and geopolitical ties.
If, for some reason, these two pairs move in the opposite direction, traders will see this as temporary and expect that they will eventually reverse back to their historical alignment. They will then sell the pair that has gone up, or overperformed, and buy the one that has gone down, or underperformed, in the hope of making money once the two get back to normal.
Advantages of mean reversion
Easy to use
Mean reversion is a simple concept and easy to implement. Beginner traders can start small, using basic tools like the Simple Moving Average, and add more indicators to refine their strategy as they learn more. Guessing is removed from the equation because you now have rules to follow.
Reliability
Some traders find that mean reversion is a more reliable strategy because it gives them concrete reasons to buy or sell. Their decisions are based on a number of tools that have together given the signal that a turn in price is likely to happen. The more overbought or oversold the asset, the greater the probability that it will reverse course.
Risk management
Since traders implementing a mean reversion strategy identify which levels are good for entering or exiting a trade, they can set limits and stop-losses at those levels. This can help to manage stress and emotion in trading. It’s also a good way to manage risk and limit losses if the price doesn’t move in the expected direction.
Potential for profit
Mean reversion can be profitable in markets that tend to remain within a certain range, like currency pairs, and sideways markets, because they will always revert to the mean and rarely break out in a sustained upward or downward trend.
Limitations of mean reversion
Signals, not guarantees
Mean reversion tools will offer signals that a price is ready to move back towards the average, but they in no way guarantee that this will actually happen. Multiple indicators and tools are combined to increase the likelihood that the trade will be successful, but anything can happen. Assets can remain overbought or oversold for a very long time before actually reversing. Prices can also move in illogical and unpredictable directions for no apparent reason.
Shocks
Sometimes, external factors and news affect prices and cause them to be re-evaluated, triggering strong, long-lasting trends. Historical data doesn’t guarantee future performance, and markets can evolve. These shocks can appear out of nowhere, interrupting patterns and trends, leading to losses.
Volatility
You need higher volatility for mean reversion trading to be more profitable. Extreme price changes don’t happen as often, either, so you have to be aware and available when they do. One way to make up for low volatility is to trade with more capital, but then you also have more to lose.
Timing
Being right about a reversal isn’t enough: you also have to get the timing right. If you enter the trade too early and the price doesn’t reverse, you can trigger your stop-loss if you set one, or miss out on more profit. Using leverage can be very risky in this situation, because if the trend stays in the wrong direction for too long, you risk having your account wiped out before the price actually reverses.
Not for every market
The mean reversion strategy doesn’t pay off in every market. Crypto markets are very volatile and will often move in extreme, unpredictable directions, pulling prices away from the mean for long periods of time. In markets like tech, breakouts can signal a new trend and drive prices upwards. In these cases, it can take months before the price reverses back to the mean. This is the case for stocks like Nvidia.
Final thoughts
Mean reversion provides a structured way to trade and is widely implemented in many different strategies. It’s usually focused on the shorter-term, and is commonly used in day trading, swing trading, and Forex trading. Because of the risks associated with this type of strategy, it’s important for traders to balance it out with disciplined risk management techniques. Since this strategy is also rooted in technical analysis and is based on price movement and indicators, some traders even resort to programming algorithms that will execute their trades on their behalf once the conditions are met. You can start slow and build up your strategy as you gain more knowledge.
Open an FBS account
By registering, you accept FBS Customer Agreement conditions and FBS Privacy Policy and assume all risks inherent with trading operations on the world financial markets.