Understanding the trading plan
The trading plan combines trading rules and creates an algorithm you will follow. Thus, the fundamental goal of a plan is to help you achieve your personal goals in trading. Let’s say that your №1 goal is to prevent severe losses. Then your trading plan should contain a part where you stop trading and take a break after a series of bad trades. You can even change your trading strategy in case of a prolonged losing streak, which would also be a part of the trading plan.
Trading plans can be very lengthy and contain a ton of different specs. However, a simple trading plan isn’t always a bad one. If you make a long-time investment, you can define to the amount of money you’re willing to invest monthly, your yield expectations, and your actions in case of prolonged losses. This plan will work perfectly, especially in the global stock market, which tends to grow over time. Still, this trading plan doesn’t have a time limit, which means there’s a possibility of holding assets for years or even decades before seeing any profits.
Swing and day traders have lengthy plans that include various specs of a trading routine. With a plan, a trader can easily define whether a trade is worth it, perform an action and control the result to the maximum degree. Even if a trade goes in another direction, with a trading plan, you can minimize risks.
Examples of a trading plan
The figure below is an example of a trend-based trading plan. Notice that this plan doesn’t include many essential parts — timing, risk management, exit points, timeframe, and type of asset. However, this example is a good place to start from.
Your trading plan should be organized like a one-stop shop, with everything you need in one place. We suggest including as much detail in your plan as possible because your results will depend on it. If you are in a shaky situation, your trading plan should always have an instruction you will follow.
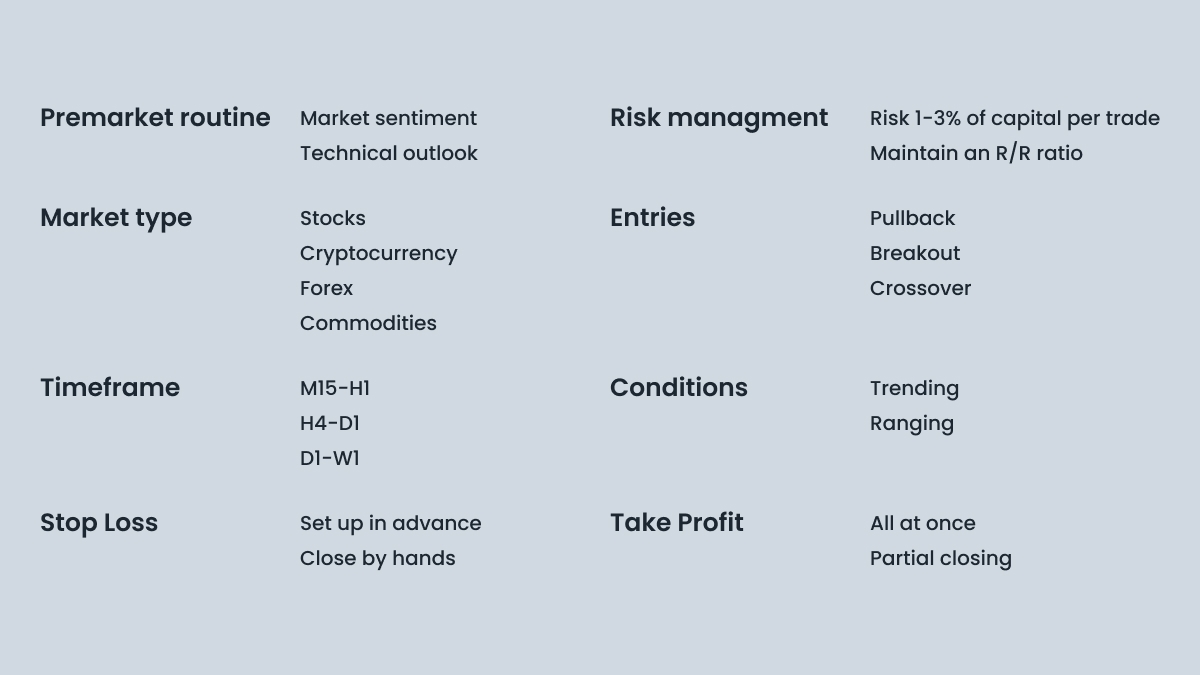
Here are the items a well-prepared and comprehensive trading plan should contain:
Premarket routine. What do you do before trading starts? Maybe you read all the fresh news and decide what asset you will choose today? Or do you look through every asset you trade and mark support and resistance lines? In both cases, your premarket routine helps you to concentrate on trading and discard everything that may distract you. Develop a routine that you follow to build discipline and consistency, and outline it in your trading plan. Then, follow this routine every day.
Timeframe. Trading on bigger timeframes is different from short-term scalping or day trading. Some trading strategies, like the “gap-and-go,” tend to work better on small M5-M15 timeframes, while others, like trend trading, work better across H4-MN (one month). This doesn’t mean you will lose your money trying to catch a trend on an M5 timeframe, but it’s way harder, especially on the Forex market, where sideways movement is the most often seen. Notice that some traders use every timeframe and don’t see a difference between trading on M5 and H4. If you are among them, you can skip this step and move to the next one.
Risk management. This is an essential part. Proper risk management will prevent you from losing all your money in one bad day, and take your trading strategy to a new level.
To improve your risk management, you need to set a daily drawdown – a potential loss after which you stop trading and begin to analyze your mistakes. Usually, traders set a 5-10% daily drawdown, after which they stop opening trades for the rest of the day.
Also, a trader should define how much money he is allowed to lose in a single trade. For me, it’s 3% of capital per trade, but more conservative traders often stick to 1% of capital per trade. It means you need to have 100 bad trades in a row to blow up your account, and you will never have 100 losses if your trading strategy is profitable.
Finally, it would be best if you had a decent risk/reward ratio. The R/R ratio measures expected income and losses in investments and trades. I suggest having at least a 1:1.5 R/R ratio. This way, for potential loss X, your profit in every trade is 1.5X. However, traders who don’t set a stop-loss and take-profit levels beforehand may skip this part if their trading plan allows it.
Define whether you will trade a trend or a range. There is a vast difference. Trend traders may hold an open position for longer because trends tend to continue. Thus, these traders may have bigger profits with fewer risks. On the other hand, range traders benefit more from sideways movements and consolidations.
Market type. A stock market is open only for specific hours, and you must be in front of your trading platform on time every weekday. The cryptocurrency market is trading 24/7, and you shouldn’t leave your order without a stop-loss due to its high volatility. The Forex market is open 24/5 (without weekends), but the volatility is lower. And that’s not to mention different macroeconomic events that influence these markets. Choose whatever you like the most: it’s way easier to trade an asset you are interested in.
You need to look for the same movements on the market and enter the trade only if it has been written in your trading plan. There are several options for an entry point:
A pullback is a perfect time to buy in case of an uptrend.
A real breakout suits those who want more certain confirmation of a movement. However, a false breakout is a thing to be aware of.
If you use technical indicators in your trading, like MACD, you can enter the trade on a crossover of indicator lines.
You can create your own entry signal. For example, it could be a divergence on the RSI oscillator, a touch of a Fibonacci retracement level, or a candlestick pattern. Still, it’s better to have several reasons to enter the trade and don’t rely only on one pattern or a technical indicator.
Stop-loss. Every trader must have a plan if things get bad. You can set a Stop Loss before entering the trade and forget about the chart while the order is open. Conversely, you can monitor your trade and decide where and when you want to exit it. This approach is way riskier as you can make emotionally-driven decisions and lose money in a potentially profitable trade.
Take-profit. If you have a risk-to-reward ratio, your take profit is further than your stop-loss. However, you can close part of your position at the first target and then move your stop-loss to breakeven. This way, your trade becomes risk-free, and you can hold it for much longer, potentially increasing your profits.
The figure below will help you as you create your trading plan.
Tactical or active trading plans
Many investors use automated investing to put a certain amount of money each month into mutual funds or other assets. Such trading plans are called automatic. While the process runs on its own, it still needs to be written down as a plan.
If a trading plan marks a condition where you will look for entries, such plans are called tactical or active. Unlike automatic investing, where the investor buys securities at regular intervals, a tactical trader typically looks to enter and exit positions at certain price levels or only when particular requirements are met. Because of this, active trading plans are much more detailed.
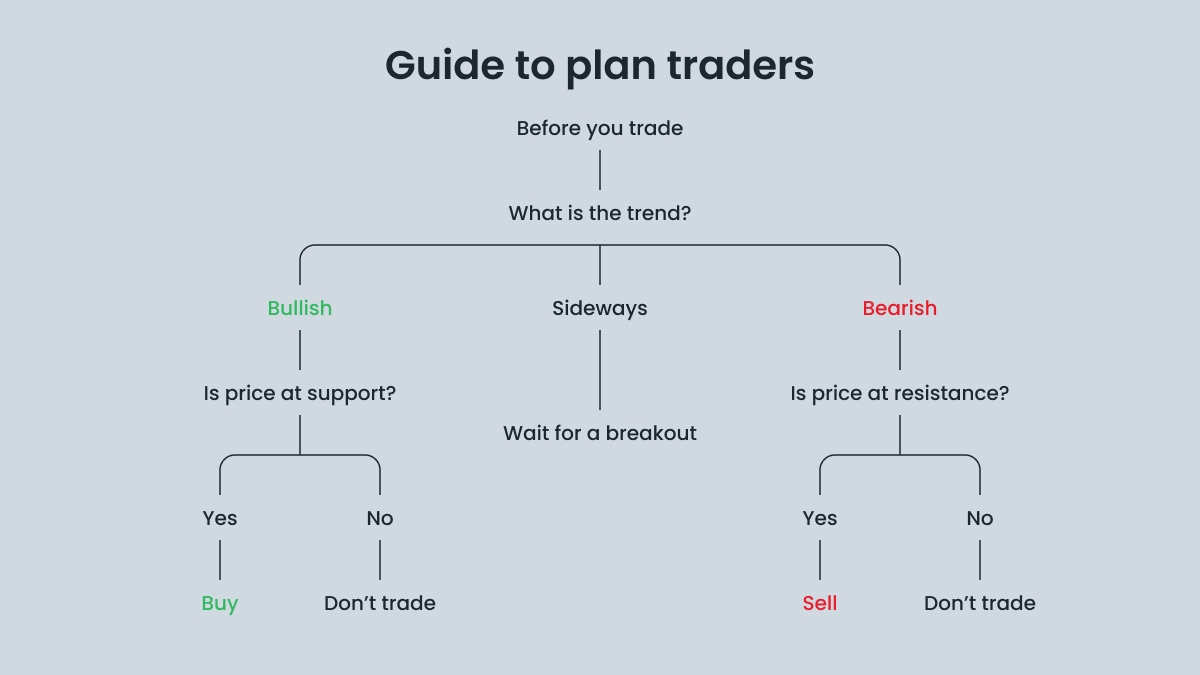
A tactical trader needs to see a set of triggers to enter the trade. Some but not all are technical indicator signals, statistical bias, or economic releases. The chapter “Examples of a trading plan” is about tactical plans, which suit traders better.
Altering a trading plan
A good trading plan doesn’t need to be changed for a long time. Usually, it covers all circumstances you may face while working with the market. Therefore, you shouldn’t change your trading plan when you have a losing streak or a bad day because your trading plan contains information about how to act in a situation like this.
However, as traders, we must improve and strive to develop our skills and knowledge. If you grow out of your old trading plan, it’s wise to develop it or create a new one that reflects a fresh market view. Notice that you should stay away from trades until the new trading plan is ready.
Trading restrictions
The main rule of a trading plan is to follow it. You need to describe every step you make to be profitable. Moreover, if your trading plan is based on technical indicators, you can make it an algorithmic trading strategy.
.jpg)